What is seropositive
rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
Patients who are seropositive for
both anti CCP and RF may have
more severe RA.1
Seropositivity refers to the presence of at
least one of two autoantibodies, rheumatoid
factor (RF) or anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide
antibody (anti-CCP), in your patient’s blood.1
40%–60% of patients with RA
are positive for both anti-CCP
and RF autoantibodies.2
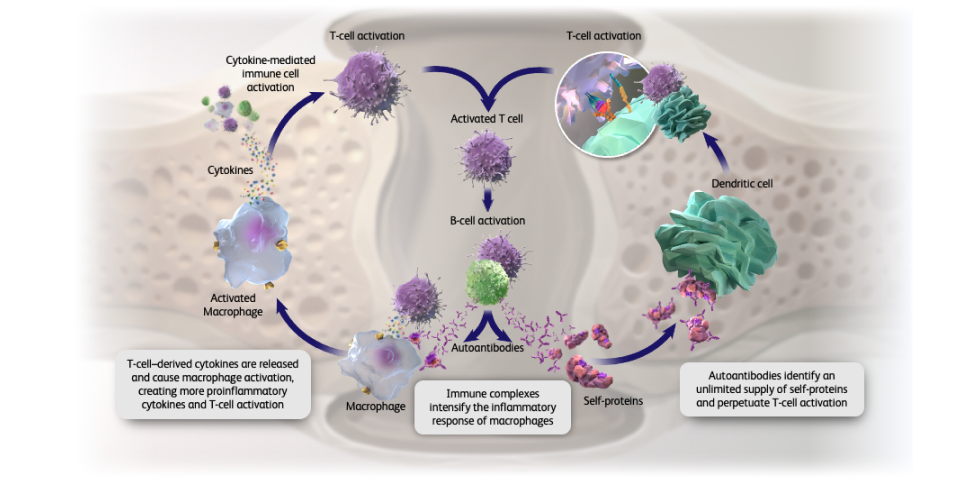
Cytokine production
Proinflammatory cytokines are
released from activated macrophages
and T cells.1
Activated T cell

Activated B cell
Autoantibody production
Activated B cells trigger production of
autoantibodies including rheumatoid
factor (RF) and anti-CCP.1
Both proinflammatory cytokines
and autoantibodies contribute to
joint
erosion, chronic
inflammation, and the destructive
cycle of RA.1
How do autoantibodies and cytokines play a
role in RA pathogenesis?1-3
Seropositivity can impact the
severity
of your patients' RA
References:
1. Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18001. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2018.1
2. Niewold TB, Harrison MJ, Paget SA. Anti-CCP antibody testing as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 2007;100:193-201.
3. Mosser DM, Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation [published correction appears in Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 Jun;10(6):460]. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12):958-969. doi:10.1038/nri2448